Timeline
- Home
- Timeline
Chronological milestones from birth to martyrdom.
From Birth to Martyrdom: A Chronological Journe
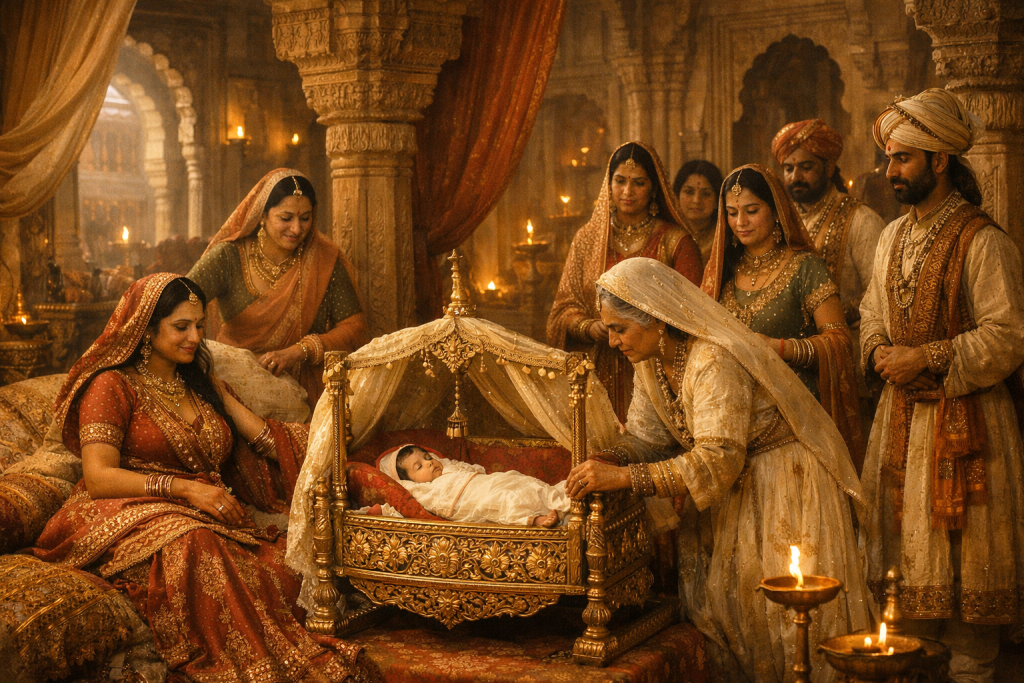

Rani Durgavati was born into the Chandela Rajput dynasty, inheriting courage, leadership, and royal dignity from childhood.
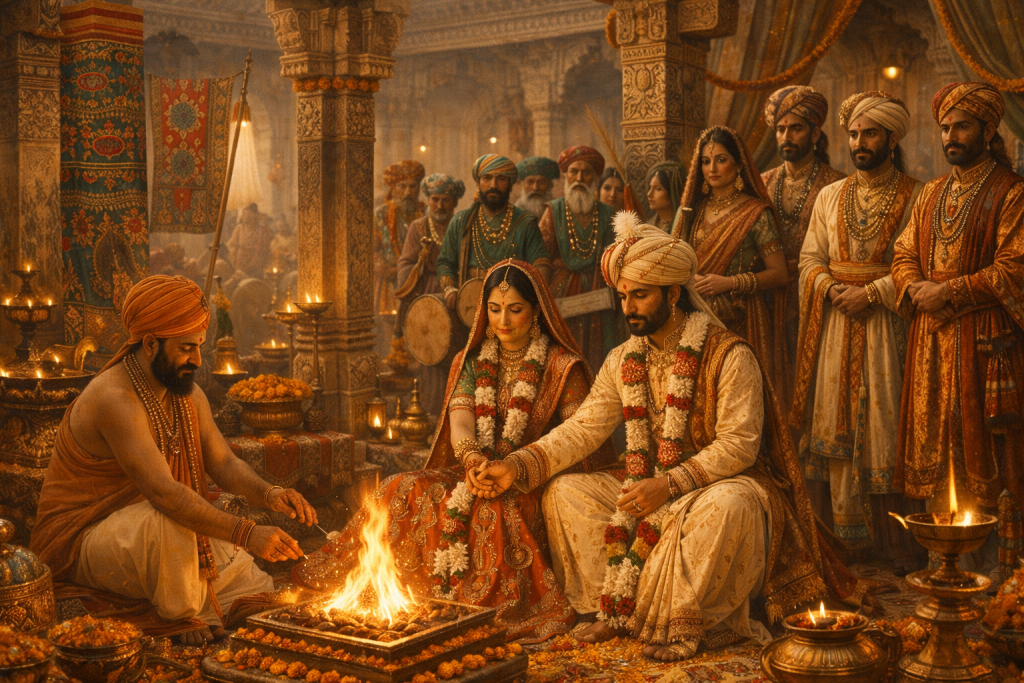

Married Dalpat Shah of Gondwana, she later assumed the throne, becoming one of central India’s most capable women rulers.
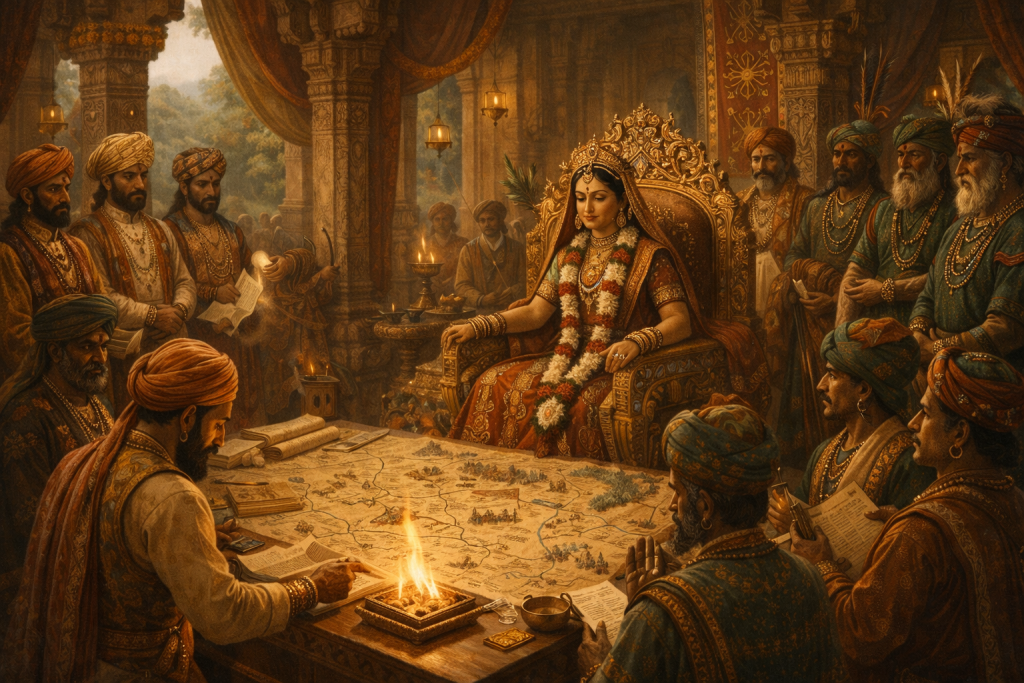

Rani Durgavati strengthened administration, protected her people, and expanded prosperity across the Gondwana kingdom.
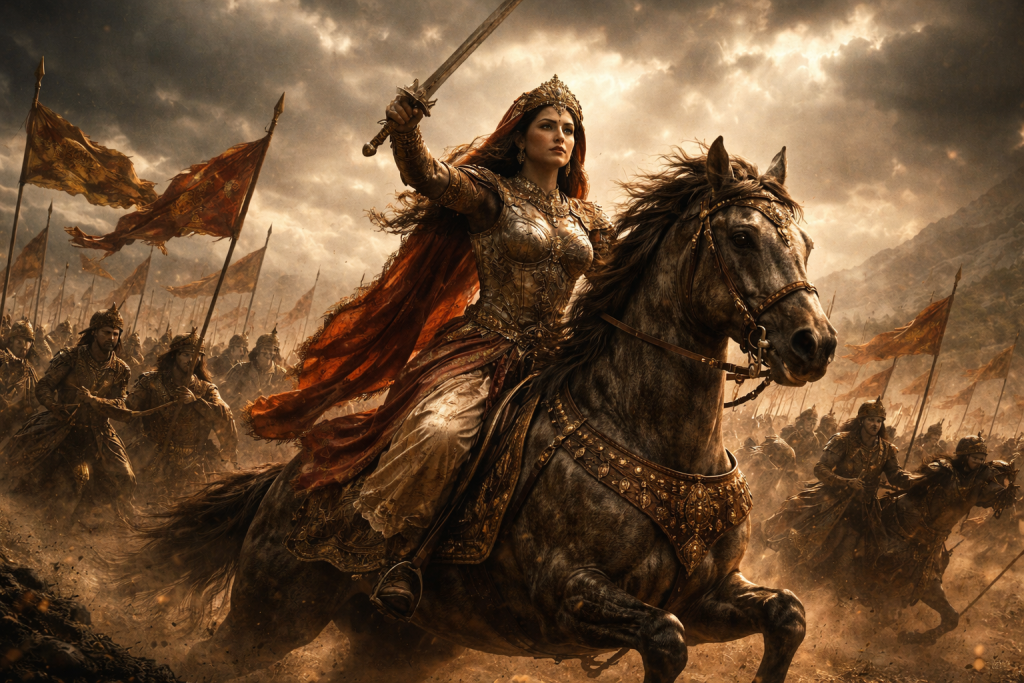

Facing Mughal general Asaf Khan, she led her army with unmatched bravery, refusing surrender despite overwhelming odds.
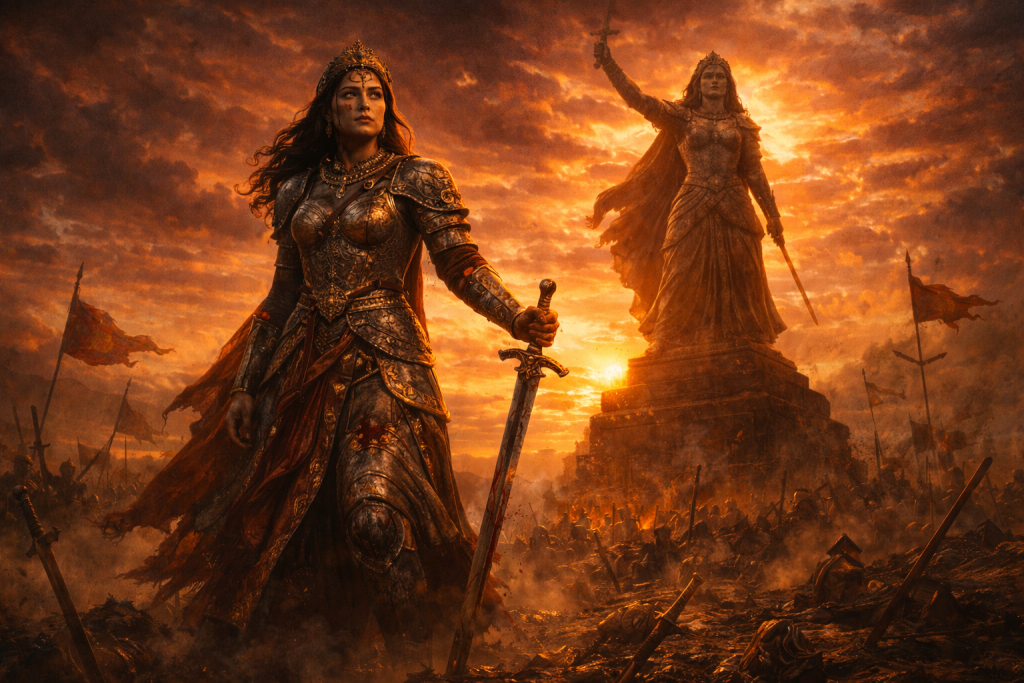

Choosing honor over captivity, Rani Durgavati attained martyrdom, becoming an eternal symbol of courage
Key battles
Key Battles That Defined Rani Durgavati’s Courage and Resistance
c. 1540–1550
Early Defense of Gondwana
Rani Durgavati strengthened Gondwana’s defenses, uniting forts and commanders to protect her kingdom from regional invasions.
1555
Battle Against Malwa Forces
She successfully resisted repeated attacks from Malwa, proving her strategic brilliance and firm leadership.
1562–1563
Resistance to Mughal Expansion
Rani Durgavati opposed Mughal advances led by Asaf Khan, refusing submission and preparing her army for war.
24 June 1564
Martyrdom of a Warrior Queen
Choosing honor over surrender, Rani Durgavati attained martyrdom, becoming an eternal symbol of courage and sacrifice.
political events
Key Political Events Shaping Rani Durgavati’s Reign and Gondwana’s Sovereignty

Ascension to Power (1550 CE)
Rani Durgavati assumed regency of Gondwana, strengthening administration and tribal governance.
Administrative Reforms
She introduced efficient taxation, protected farmers, and promoted justice across her kingdom.
Fortification of Gondwana
Strategic forts and defenses were strengthened to secure political independence.

Resistance to Mughal Expansion
She firmly opposed Mughal political dominance over Gondwana territories.
turning points.
Defining Moments That Shaped Rani Durgavati’s Courageous Reign

Ascension as Queen Regent (1550)
After King Dalpat Shah’s death, Rani Durgavati assumed regency, ruling Gondwana with wisdom, strength, and administrative skill.
Strengthening Gondwana’s Administration
She reorganized revenue systems, promoted agriculture, and ensured justice, earning loyalty from her people and nobles.
Defense Against Early Mughal Pressure
Rani resisted growing Mughal influence, maintaining Gondwana’s independence despite repeated warnings and political pressure.
Alliance Building with Local Chiefs
She forged strategic alliances with neighboring rulers and tribal chiefs to strengthen military and political unity.
Battle of Narrai (1564)
Facing Asaf Khan’s Mughal forces, Rani chose resistance over surrender, leading her army personally into battle.
Martyrdom and Immortal Legacy
Refusing capture after being wounded, Rani Durgavati embraced martyrdom, becoming a timeless symbol of courage and self-respect.

